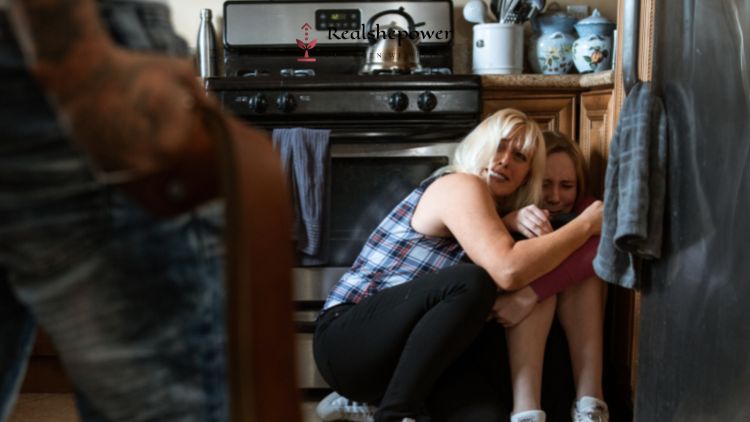Is Domestic Violence a Felony in the United States?


Domestic violence is a serious and widespread issue in the United States. Despite increased awareness and efforts to address the problem, millions of individuals still fall victim to this form of abuse each year. The legal consequences for committing domestic violence can vary widely depending on the state in which the crime was committed and the severity of the abuse. In this article, we will explore the issue of domestic violence, is domestic violence a felony in the United States, and the factors that influence a state’s decision to classify it as a felony.
Table of Contents
Explanation of What Domestic Violence is and Its Prevalence in the United States
Domestic violence, also known as intimate partner violence, is a pattern of behavior that involves the use of physical, psychological, or sexual abuse to control and intimidate a current or former partner.
This type of violence affects millions of individuals in the United States each year, regardless of their gender, race, ethnicity, sexual orientation, or socioeconomic status.
According to the National Domestic Violence Hotline, approximately 20 people are physically abused by an intimate partner every minute in the United States.
For example, in 2018, over 7 million cases of domestic violence were reported in the United States.
Overview of Potential Punishments for Committing Domestic Violence
The punishment for domestic violence can vary widely depending on the severity of the crime, the state in which it was committed, and the individual circumstances of the case.
In some states, domestic violence is classified as a misdemeanor, which is a less serious crime that is typically punished with a fine, community service, or a short term in jail. For example, in California, a first-time domestic violence conviction is generally considered a misdemeanor, punishable by up to one year in jail and a fine of up to $2,000.
In other states, domestic violence is classified as a felony, which is a more serious crime that is typically punished with a long-term imprisonment or other severe penalties. For example, in Texas, a domestic violence conviction can result in a prison sentence of up to 20 years and a fine of up to $10,000.
Definition of a Felony and Consideration of Whether Domestic Violence Fits the Classification
A felony is defined as a serious crime that is punishable by imprisonment for a term of one year or more. In general, crimes such as murder, robbery, and sexual assault are considered felonies.
Domestic violence is a crime that can involve physical violence, sexual abuse, and psychological manipulation, making it a complex and serious issue.
Depending on the severity of the crime, the state in which it was committed, and the individual circumstances of the case, domestic violence can be classified as either a misdemeanor or a felony.
Description of Relevant Factors and Laws That Influence a State’s Decision to Charge Domestic Violence as a Felony
The decision to charge domestic violence as a felony is influenced by several factors, including the severity of the crime, the individual circumstances of the case, and state laws.
For example, some states have enacted laws that mandate that domestic violence be charged as a felony if the victim is pregnant, if the perpetrator has a prior history of domestic violence, or if the abuse involves a weapon.
In California, for instance, if a domestic violence case involves the use of a deadly weapon, the perpetrator can be charged with a felony and face a prison sentence of up to 4 years.
In addition, some states have adopted laws that allow prosecutors to charge domestic violence as a separate and distinct crime, rather than as a part of a larger criminal case. This makes it easier for prosecutors to secure a conviction and ensures that domestic violence is taken seriously by the criminal justice system.
Summary of the Overall Legal Impact of Domestic Violence Being Classified as a Felony
Domestic violence is a serious crime that can have a profound impact on the lives of victims and their families.
When domestic violence is classified as a felony, it sends a message that this type of crime will not be tolerated and that those who commit it will face severe consequences.
This can also serve as a deterrent to potential perpetrators, as they are more likely to be held accountable for their actions if they are convicted of a felony.
For example, in many states, a domestic violence conviction can result in a loss of firearms rights, which can help prevent future acts of violence.
Additionally, a domestic violence conviction can have long-lasting consequences for the perpetrator, such as difficulties obtaining employment or housing, or even immigration consequences if they are not a U.S. citizen.
More on Domestic violence
You can now write for RSP Magazine and be a part of the community. Share your stories and opinions with us here.